AIR QUALITY
IN SOUTH DAKOTA
Radon
The Department of Agriculture and Natural Resources (DANR) will provide 500 free Radon test kits to South Dakota Residents. These kits will allow you to test the Radon levels in your home. Get your free test kit here .
What is Radon
Radon is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas. It is formed as natural deposits of uranium throughout the earth's crust decay. As radon decay products are inhaled, they can alter the cells in the lungs. These alterations can increase the potential for getting lung cancer. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer behind smoking. An estimated 14,000 people die of radon related lung cancer each year.
The amount of radon in a building is dependent upon several factors. These factors include the geology, a driving force, pathways into the building, and the ventilation rate. As the concentration of uranium is in the underlying soil increases, so does the strength of the radon. Radon is transported to buildings more easily through permeable soils. Buildings can create pressure differentials that will draw in the soil gases. Radon can enter the building through many paths such as cracks in the foundation, utility penetrations, sumps, and floor drains. The ventilation rate of the building affects the final radon concentration.
EPA has made the recommendation of no long-term radon exposures above 4 pico couries/liter (pCi/L). This action level was based on both health and economics. The only way to tell if a building has elevated levels of radon is to have it tested. Test kits are inexpensive and easy to use.
South Dakota Levels
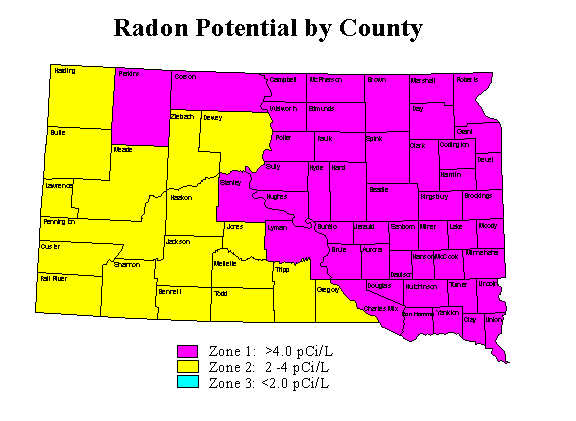
Since the late 1980's, radon levels have been measured throughout the state of South Dakota. This data has been collected and compared to geological formations to yield the map shown below. The zone classifications are based upon being able to predict the likelihood of finding certain ranges of radon concentrations when conducting short-term radon measurements. The eastern portion of the state is Zone 1 with the balance being Zone 2. There are no Zone 3 areas in South Dakota.
These maps should not be used as a substitute for an actual radon test. The only way to determine radon concentrations in a building is to test.
United States Levels
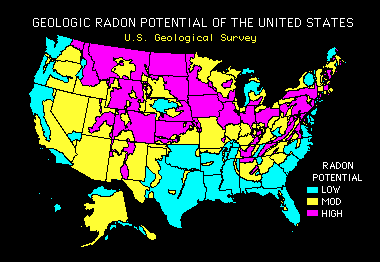
Radon is not a concern isolated only in South Dakota. The map below shows the geologic radon potential for the United States. These maps should not be used as a substitute for an actual radon test. The only way to determine radon concentrations in a building is to test.
How to Test for Radon
There are two different types of radon tests:
- Passive tests: A passive device does not require electricity or power to operate. It has the advantage of being very inexpensive, but it does not provide an indication of changes during the test period. It usually requires laboratory analysis to determine the radon level. Some examples of passive devices include: activated charcoal canisters, alpha track detectors, and electret ion chambers.
- Active tests: Active monitors are more sophisticated devices that utilize electronics to provide an hour by hour reading of radon variations. These monitors are more expensive to run, but usually give instantaneous results.
Both passive and active tests are acceptable methods of testing. The choice of which type to use is largely a personal decision, based on factors such as cost and timing. No matter what type of test is used, it should meet EPA proficiency standards. Passive tests can be purchased at some local hardware stores or online.
The test kit should be placed in lowest livable level of the house. It should be placed in a room that is frequently occupied, but where high humidity would not be expected. Good locations would include bedrooms and family rooms. The minimum distances for a test device are: at least 20 inches from the floor, 4 inches from another object, 12 inches from an exterior wall, and 3 feet from an outside window.
These tests should be run under "closed-house" conditions. This means that exterior doors and windows should be kept shut for 12 hours before and during the test, except for normal walking in and out. Fan and blowers should be turned off. Air conditioners can be used, but not on the "fresh air" setting.
At the end of the testing time, the kit should be returned to the lab for analysis.
Click here for a list of residential measurements service providers certified by the National Radon Proficiency Program (NRPP) or Click here for a list of residential measurement service providers certified by the National Radon Safety Board (NRSB).
Mitigation of Radon
If you find that your home has high radon levels, there are ways to reduce the concentrations. Even very high levels can be reduced to acceptable levels. There are several methods that can be used to lower radon levels in your home. Some techniques prevent radon from entering your home while others reduce radon levels after it has entered. EPA generally recommends methods which prevent the entry of radon. One method that prevents the entry of radon into your home is called active soil depressurization. This system consists of pvc pipe connected to the soil either through a hole in the slab, a sump lid connection or beneath a plastic sheet in a crawl space. Attached to the pipe is a quiet, continuously operating fan that discharges the radon to a safe location outside of the home.
- Average installation cost: $1,200
- Average operating cost in South Dakota:$3.00/month
- Expected life span of fan: 11 years
- Fan replacement cost: $145 - $300
Click here for a list of residential mitigation service providers certified by the National Radon Proficiency Program (NRPP) or click here for a list of residential mitigation service providers certified by the National Radon Safety Board (NRSB).
For More Information on Radon and Related Internet Links
1-800 Numbers
- DANR Radon Information Line 1-800-438-3367
- National Radon Information Line 1-800-SOS-RADON (1-800-767-7236)
- Radon FIX-IT Program 1-800-644-6999
- US EPA Radon Home Page - EPA maintains a radon information site with many resources for both individuals and businesses. You can read or print any of EPAs radon publications.